Caffeine (CAS 58-08-2) – Wholesale & Research Grade
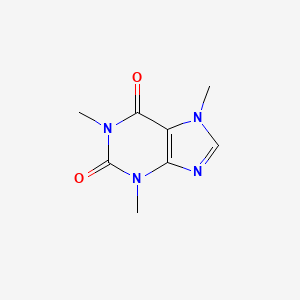
Caffeine is a trimethylxanthine in which the three methyl groups are located at positions 1, 3, and 7. A purine alkaloid that occurs naturally in tea and coffee. It has a role as a central nervous system stimulant, an EC 3.1.4.* (phosphoric diester hydrolase) inhibitor, an adenosine receptor antagonist, an EC 2.7.11.1 (non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase) inhibitor, a ryanodine receptor agonist, a fungal metabolite, an adenosine A2A receptor antagonist, a psychotropic drug, a diuretic, a food additive, an adjuvant, a plant metabolite, an environmental contaminant, a xenobiotic, a human blood serum metabolite, a mouse metabolite, a geroprotector and a mutagen. It is a purine alkaloid and a trimethylxanthine.
Research Context
Caffeine, a well-known stimulant commonly found in coffee and tea, has garnered significant attention in research due to its diverse applications and effects on human health. Beyond its role as a popular beverage ingredient, caffeine is being studied for its potential benefits in enhancing cognitive function, improving athletic performance, and offering neuroprotective properties.
Research Applications
In clinical studies, caffeine has demonstrated the ability to improve alertness and concentration, making it a focal point in research related to attention-deficit disorders and sleep deprivation. Furthermore, its ergogenic effects have made it a subject of interest in sports science, where it is often analyzed for its impact on endurance and strength performance. Additionally, ongoing research is investigating caffeine's role in reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic agent.
Mechanism of Action
Caffeine primarily functions as an adenosine receptor antagonist, blocking the inhibitory neurotransmitter adenosine and promoting increased neuronal firing. This mechanism leads to heightened alertness and improved mood. Moreover, caffeine stimulates the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and norepinephrine, further contributing to its stimulatory effects. Understanding these pathways provides insights into how caffeine can be harnessed for therapeutic applications, particularly in mental health.
Solubility and Storage Advice
Caffeine is soluble in water, alcohol, and many organic solvents, which facilitates its use in various formulations, including beverages and pharmaceuticals. For optimal stability, caffeine should be stored in a cool, dry place away from light. It is crucial to keep it sealed in an airtight container to prevent degradation and maintain potency.
Future Research Directions
Future studies are likely to focus on elucidating the long-term effects of caffeine consumption on health, particularly its interaction with different genetic backgrounds regarding metabolism and sensitivity. Additionally, research may explore the potential of caffeine as a delivery system for other therapeutic agents, enhancing its applicability in medical treatments. The ongoing investigation into caffeine's role in mental health and performance optimization continues to open new avenues for exploration in both scientific and consumer contexts.
| CAS Number | 58-08-2 |
|---|---|
| Formula | C8H10N4O2 |
| Mol. Weight | 194.19 g/mol |
| IUPAC Name | 1,3,7-trimethylpurine-2,6-dione |
| Grade | HPLC ≥98% |
Synthesis & Storage
Caffeine is supplied as a lyophilized powder to ensure stability during transit.
For long-term storage of CAS 58-08-2, we recommend maintaining at -20°C.
Researchers must reconstitute this peptide with bacteriostatic water or sterile solvent only when ready for use.
Quality Control: All batches undergo rigorous HPLC purity testing (≥98%) prior to dispatch from our USA fulfillment center.