Eptifibatide (CAS 188627-80-7) – Wholesale & Research Grade
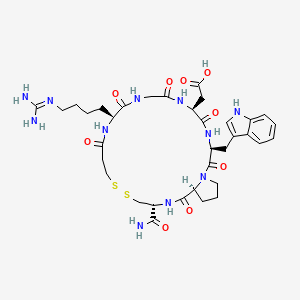
Eptifibatide is a synthetic homodetic cyclic peptide comprising N(alpha)-(3-sulfanylpropanoyl)homoarginyl, glycyl, aspartyl, tryptophyl, prolyl and cysteinamide residues connected in sequence and cyclised via a disulfide bond. Derived from a protein found in the venom of the southeastern pygmy rattlesnake, Sistrurus miliarus barbouri, eptifibatide is an anti-coagulant that inhibits platelet aggregation by selectively blocking the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor, so preventing the binding of fibrinogen, von Willebrand factor, and other adhesive ligands. It is used in the management of unstable angina and in patients undergoing coronary angioplasty and stenting procedures. It has a role as a platelet aggregation inhibitor and an anticoagulant. It is an organic disulfide, a macrocycle and a homodetic cyclic peptide.
Research Context
Eptifibatide, a potent antiplatelet agent known for its role in inhibiting platelet aggregation, has garnered significant attention in the field of cardiovascular research. This cyclic heptapeptide is primarily utilized in the treatment of acute coronary syndromes and during percutaneous coronary interventions. Its ability to selectively bind to glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptors on platelets makes it a critical component in the management of thrombotic disorders.
Research Applications
In clinical settings, Eptifibatide is employed to reduce the incidence of myocardial infarction and improve outcomes during coronary procedures. Research continues to explore its efficacy in various populations, including patients with diabetes and those undergoing high-risk angioplasty. Additionally, studies are investigating the drug's potential in combination therapy with other antithrombotic agents to enhance overall therapeutic outcomes.
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of Eptifibatide involves the reversible inhibition of the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor, which plays a pivotal role in platelet aggregation. By blocking this receptor, Eptifibatide effectively prevents fibrinogen from binding to activated platelets, thereby reducing clot formation and stabilizing the thrombus. This targeted action contributes to its effectiveness in acute coronary events.
Solubility and Storage Advice
Eptifibatide is soluble in water, which facilitates its administration in clinical settings. It is important to store Eptifibatide at controlled room temperature, away from light and moisture, to maintain its potency and efficacy. Proper storage conditions are crucial for ensuring the stability of this therapeutic agent over its shelf life.
Future Research Directions
- Investigating the long-term outcomes of Eptifibatide in diverse patient demographics.
- Exploring its role in outpatient settings and its potential for reducing healthcare costs.
- Assessing combination therapies involving Eptifibatide to further enhance cardiovascular protection.
As research continues, Eptifibatide's role in cardiovascular medicine may expand, leading to novel applications and improved patient care strategies.
| CAS Number | 188627-80-7 |
|---|---|
| Formula | C35H49N11O9S2 |
| Mol. Weight | 832.0 g/mol |
| IUPAC Name | 2-[(3S,6S,12S,20R,23S)-20-carbamoyl-12-[4-(diaminomethylideneamino)butyl]-3-(... |
| Grade | HPLC ≥98% |
Synthesis & Storage
Eptifibatide is supplied as a lyophilized powder to ensure stability during transit.
For long-term storage of CAS 188627-80-7, we recommend maintaining at -20°C.
Researchers must reconstitute this peptide with bacteriostatic water or sterile solvent only when ready for use.
Quality Control: All batches undergo rigorous HPLC purity testing (≥98%) prior to dispatch from our USA fulfillment center.