Uric Acid (CAS 69-93-2) – Wholesale & Research Grade
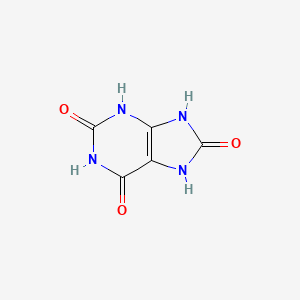
7,9-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6,8(3H)-trione is an oxopurine in which the purine ring is substituted by oxo groups at positions 2, 6, and 8. It has a role as a human metabolite, an Escherichia coli metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is a tautomer of a 2,6-dihydroxy-7,9-dihydro-8H-purin-8-one, a 9H-purine-2,6,8-triol, a 7H-purine-2,6,8-triol, a 1H-purine-2,6,8-triol and a 5,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6,8(9H)-trione.
Research Context
Uric acid, a naturally occurring compound in the body, plays a significant role in various biological processes and has garnered attention in multiple research applications. It is primarily known for its role as an end product of purine metabolism, and its levels can serve as a biomarker for several health conditions, including gout and cardiovascular diseases. Recent studies have highlighted the antioxidant properties of uric acid, suggesting its potential in mitigating oxidative stress-related disorders.
Mechanism of Action
The biological activities of uric acid are largely attributed to its ability to scavenge free radicals, thereby protecting cells from oxidative damage. This mechanism is crucial in understanding its dual role as both a potential protective agent and a contributor to disease when present in elevated concentrations. Research has indicated that uric acid may influence inflammatory pathways, offering a target for therapeutic interventions in conditions like hypertension and metabolic syndrome.
Solubility and Storage Advice
Uric acid exhibits low solubility in water, which can lead to crystallization in physiological environments. When handling uric acid in a laboratory setting, it is recommended to store it in a cool, dry place to maintain its stability. For optimal results, solutions should be prepared fresh and used promptly to avoid degradation. It is also advisable to conduct experiments under controlled pH conditions to prevent precipitation, which can interfere with analytical results.
Future Research Directions
- Investigation of uric acid's role in metabolic disorders and its potential as a therapeutic target.
- Exploration of its antioxidant properties and implications for aging and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Development of novel methods to modulate uric acid levels in clinical settings for improved patient outcomes.
As research progresses, understanding the complex roles of uric acid will continue to unveil new therapeutic avenues and enhance our knowledge of its impact on human health.
| CAS Number | 69-93-2 |
|---|---|
| Formula | C5H4N4O3 |
| Mol. Weight | 168.11 g/mol |
| IUPAC Name | 7,9-dihydro-3H-purine-2,6,8-trione |
| Grade | HPLC ≥98% |
Synthesis & Storage
Uric Acid is supplied as a lyophilized powder to ensure stability during transit.
For long-term storage of CAS 69-93-2, we recommend maintaining at -20°C.
Researchers must reconstitute this peptide with bacteriostatic water or sterile solvent only when ready for use.
Quality Control: All batches undergo rigorous HPLC purity testing (≥98%) prior to dispatch from our USA fulfillment center.